 |
 |
Posters Links |
|
|
 |
| Recent Posters |
|
 |
 |
| |
  |
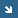
BROADBAND_CLOUDS:
A TOOL FOR 2D REPRESENTATION OF CLOUDS IN MIPAS/ENVISAT
SCENARIO, DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS. (ASSFTS '09)
|
 |
The Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric
Sounding (MIPAS), operating on-board ENVISAT, is a
limb sounding Fourier Transform spectrometer for the
measurement of high resolution gaseous emission spectra.
Studies on MIPAS data have demonstrated its sensitivity
to the radiation emitted from the clouds.
The GMTR forward model has been used to create a self-standing
Broad Band (BB) forward model (capable to simulate
extended spectral regions). We have introduced into
the BB forward model the capability to model the effects
of cloud contamination into MIPAS spectra (BB_Clouds).
Exploiting the 2D approach, the cloud is no longer
represented as an infinite cloudy shell, but it is
characterized by both a vertical and a horizontal
extension. BB_Clouds has been used to assess the possibility
to retrieve cloud extension and other parameters from
MIPAS spectra. The developed algorithm and the results
of the tests performed are presented and discussed.
|
 |
| |
  |
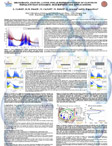
RETRIEVAL
OF H15NO3/H14NO3 VERTICAL ATMOSPHERIC DISTRIBUTION FROM
MIPAS/ENVISAT LIMB EMISSION MEASUREMENTS('08)
|
 |
Atmospheric infrared remote-sensing has the potential
to provide accurate information on the isotopic composition
of several molecular constituents. Since new precise
spectroscopic pa rameters of isotopically substituted
molecules are becoming available, further advances
in the understanding of the mechanisms leading to
atmospheric isotope fractionation are possible. MIPAS
(Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric
Sounding), on-board the European satellite ENVISAT,
is a mid-infrared emission FT interferometer probing
the Earth's atmosphere with limb- scanning observations.
The detected spectral radiances are routinely inverted
to vertical distributions of pressure, temperature,
and Volume Mixing Ratio (VMR) of H2O, O3, CH4, N2O,
HNO3, and NO2. Non-operational scientific codes have
proven that MIPAS spectra can also provide information
on minor atmospheric trace constituents as well as
on the distribution of the main isotopes in these
gases. The inclusion of H15NO3 spectral line parameters
(relative to the fundamental v5 band) into MIPAS-dedicated
spectro scopic database provided the possibility to
identify, for the first time, H15NO3 in the atmosphere
(near 871 cm-1), and to investigate the behaviour
of 15N in atmospheric nitric acid. Never before has
the heavy-to-light nitrogen isotopic ratio profile
been retrieved from HNO3 spectral signatures.
|
 |
| |
  |
Distribuzioni
verticali di Temperatura, acqua, ozono e acido nitrico
dalle misure di MARSCHALS durante la campagna SCOUT-O3
in Darwin (Nov. - Dic. 2005)
(Ischia '07)
|
 |
MARSCHALS e' uno spettrometro eterodina che misura
l'emissione termica atmosferica nel lontano infrarosso
(FIR) con la tecnica del sondaggio a lembo. Lo strumento
opera a bordo dell'aereo stratosferico M55 Geophysica.
MARC e' il codice di analisi disegnato appositamente
per l'analisi delle misure di MARSCHALS. Fra le sue
caratteristiche ci sono la possibilità di eseguire
l'analisi con la tecnica Multi-Target Retrieval (MTR)
usando tutta la banda misurata e includendo la matrice
degli errori sistematici durante la procedura di analisi.
Il codice MARC e lo strumento MARSCHALS sono stati
sviluppati durante uno studio ESA il cui obiettivo
era testare la possibilità di usare la tecnica
al lembo nel FIR per misurare la regione dell'alta
troposfera e bassa stratosfera (UTLS).
I risultati ottenuti analizzando le misure di MARSCHALS
fatte durante la campagna SCOUT-O3 in Darwin, Australia
(Nov. – Dic. 2005) verranno presentati. Sono
state ottenute le distribuzioni verticali di Temperatura,
acqua, ozono e acido nitrico nella regione UTLS lungo
la rotta di volo di Geophysica. I risultati sono stati
validati con le misure di altri strumenti a bordo
dello stesso aereo e con dati ottenuti con un modello
di chimica atmosferica.
|
 |
|
| |
  |
SOLAR INDUCED
PERTURBATIONS IN THE MIDDLE ATMOSPHERE: IS IT JUST A MATTER OF
MAGNITUDE? (EGU - April '05)
|
 |
As a first order approximation, the response
of the middle atmosphere to perturbations that are likely to
occur, is characterized by changes in the O3 distribution. In
fact, because of the peak in the O3 heating profile at about
50 Km, strong variations in the O3 concentration cause a corresponding
change in the heating of the atmosphere. As a consequence, temperature
and wind fields are changed. But what does "strong"
mean? A large drop of ozone concentration in a very stable atmospheric
region can have a weaker response than one in an unstable region.
Thus, "strong" should be considered not on the base
of the perturbation itself, but on the base of the response
to that perturbation. This study attempts to investigate the
characteristics of perturbations that may affect the atmosphere,
showing preliminary results of analyses of the response of a
middle atmospheric model. In this poster, rather than constructing
a complete set of test perturbations, we focus on a few case
studies and will later test our hypothesis on more complete
models (such as the ARPEGE - see DMI Peter Berg, poster X441
this session). Even though not directly involving solar variability,
the different scales we study may as well be considered different
scales of (indirect) solar induced perturbations.
|

 |
 |
| |
  |
MIPAS-ENVISAT
Validation Measurements with the High Resolution FT-FIR
Spectrometer SAFIRE-A aboard the Stratospheric Aircraft
M-55 Geophysica (QOS - June '04)
|
 |
The SAFIRE-A Fourier transform
Far-infrared spectrometer has been involved in field
campaigns carried out with the M-55 Geophysica stratospheric
aircraft in 2002-2003, aimed at validating the level-2
products of the ENVISAT chemistry instruments. The limb
sounding observations of volume mixing ratio vertical
profiles of Ozone and Nitric Acid were especially focused
on the validation of MIPAS products in the altitude
range 10-20 km.
Three campaigns have been conducted with the Geophysica
platform from Forlì, Italy (Lat. 44°N, Lon.
12°E) in July and October 2002 and from Kiruna,
Sweden (Lat. 68°N, Lon. 20°E) in February-March
2003, as part of the ESABC (ENVISAT Stratospheric Aircraft
and Balloon Campaigns) activities. Here, we report the
results of measurements of O3, HNO3 acquired by SAFIRE-A
during the mid-latitude flight on the 24th of October
2002.
.An attempt to further exploit SAFIRE-A mid-latitude
observations, in order to enlarge the dataset useful
for MIPAS validation has been made with the support
of modelling tools specifically developed by University
of L’Aquila. First results from intercomparison
based on trajectory calculations are presented, showing
the effectiveness of the adopted approach. |

|
|
 |
 |
| |
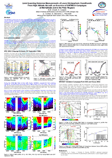  |
Limb Sounding Emission
Measurements of Lower Stratospheric Constituents
From High Altitude Aircraft: an Overview of SAFIRE-A Campaigns
at Mid-latitude and in the Polar Regions
(QOS - June '04)
|
 |
The SAFIRE-A instrument has been deployed
on the M-55 Geophysica high altitude aircraft in several scientific
campaigns carried out, between the end of 1999 and the beginning
of 2003, at mid-latitudes as well as in the Polar regions (both
Arctic and Antarctica). The measurement capabilities of the
spectrometer allowed the observation of the vertical distribution
of several minor atmospheric constituents between the tropopause
and the flight altitude (approx. 20 km) along the flight route.
Recently, an optimised retrieval code, specifically developed
for the analysis of the airborne instrument data, has been applied
for the re-processing of the data measured during the APE-GAIA
campaign (Ushuaia, Argentina, September-October 1999) and during
ENVISAT validation flights at mid-latitude (Forlì, Italy,
October 2002) and high-latitude flights (Kiruna, Sweden, March
2003). An overview of the main results is presented, highlighting
the instrument capability to simultaneously measure Volume Mixing
Ratio (VMR) vertical profiles of different species such as Ozone,
HNO3, N2O, ClO, HCl, H2O, that play a critical role in lower
stratospheric chemistry and transport. |

|
 |
 |
| |
  |
SF6 Multi-Target Retrieval
(ASSFTS - October '03)
|
 |
A retrieval approach for the simultaneous
determination of the altitude distributions of pressure (p),
temperature (T) and Volume Mixing Ratio (VMR) of atmospheric
constituents from limb scanning measurements of the atmosphere
has been developed and implemented in a computer code for the
analysis of MIPAS- ENVISAT observations [B.M.Dinelli, D.Alpaslan,
M.Carlotti, .Magnani, M.Ridolfi, 'Multi-target retrieval (MTR):
the simultaneous retrieval of pressure, temperature and volume
mixing ratio profiles from limb-scanning atmospheric measurements',
Journal of Quantum Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, in press,
(2003)]. This analysis method, named Multi-Target Retrieval
(MTR), has been used to retrieve the altitude distribution of
the SF6 VMR in the troposphere, from selected MIPAS orbits.
The SF6 profile was retrieved simultaneously with the p, T,
water and ozone profiles analysing selected spectral features
of SF6 jointly with the spectral intervals used by the ESA Level
2 processor for the sequential analysis of the MIPAS key species. |

|
 |
 |
| |
  |
Multi Target
Retrieval (EGS - April '03)
|
 |
The processes of discretization, interpolation,
and resampling are frequently used in data analysis. Here the
formalism of functional spaces is used as a framework for the
description and characterization of both the measurement operation
and these subsequent processes. The tools provided by this formalism
are applied to the problem of resampling of atmospheric volume
mixing ratio vertical profiles obtained with limb-sounding measurements.
In particular, a resampling method that uses the conservation
of the vertical column as a constraint is presented and compared
with other methods. The effects of the resampling process in
terms of error propagation and loss of vertical resolution are
also evaluated. |

|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
ISAC - CNR
Gruppo: Remote Sensing of the Stratosphere
Via P. Gobetti, 101
40129 Bologna
ITALY
Tel.+39 051 6398002
|
|
 |
|
